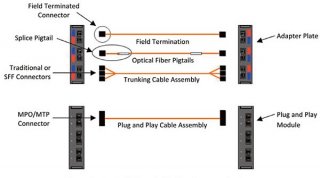
- Description
- Reviews
- FAQs
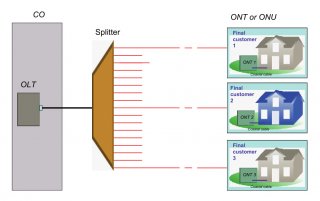
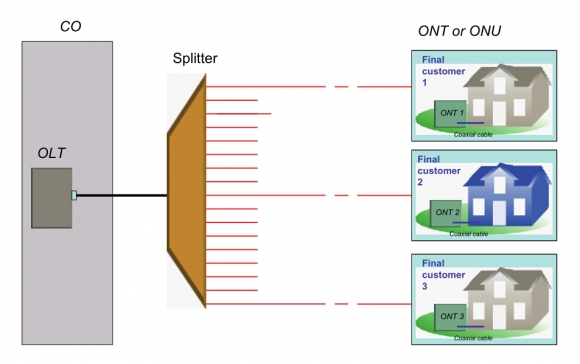
A PON network consists of an OLT connected via a PON splitter to multiple ONTs (one for each subscriber, up to 64 subscribers). Sometimes, a second splitter can be connected in cascade to the first splitter to dispatch services to buildings or residential areas, which has been introduced more clearly in the previous post “Understanding the Split Ratios and Splitting Level of Optical Splitters”. This post will tell about troubleshooting of a point-to-multipoint FTTH network, also defined as a PON network.
PON Fault Scenarios
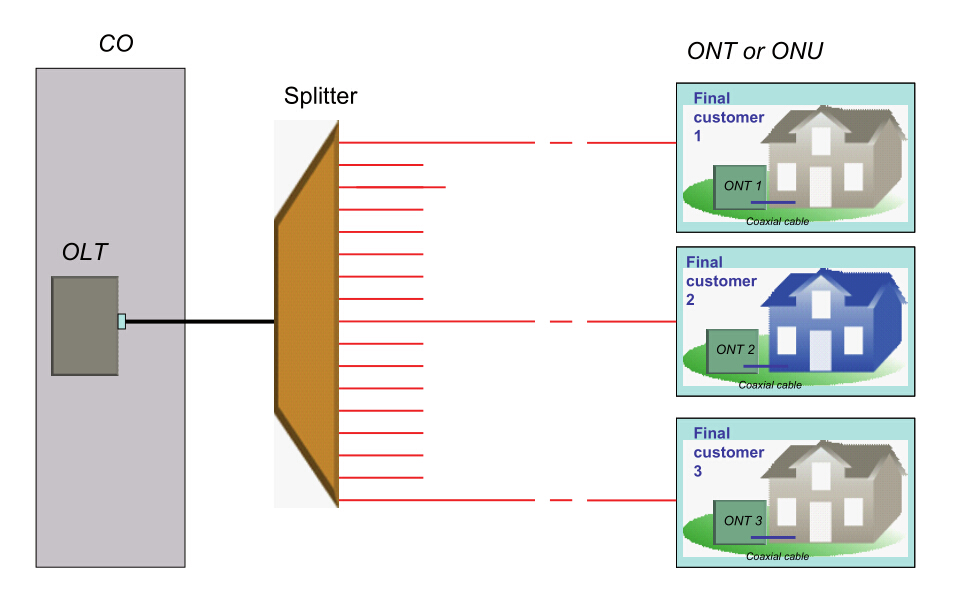
Scenario 1: Simple PON (only one customer is affected)
There are three potential faults when only one subscriber cannot receive service—fault in the distribution fiber between the customer and the closest splitter, or fault in the ONT equipment, or fault in the customer’s home wiring.
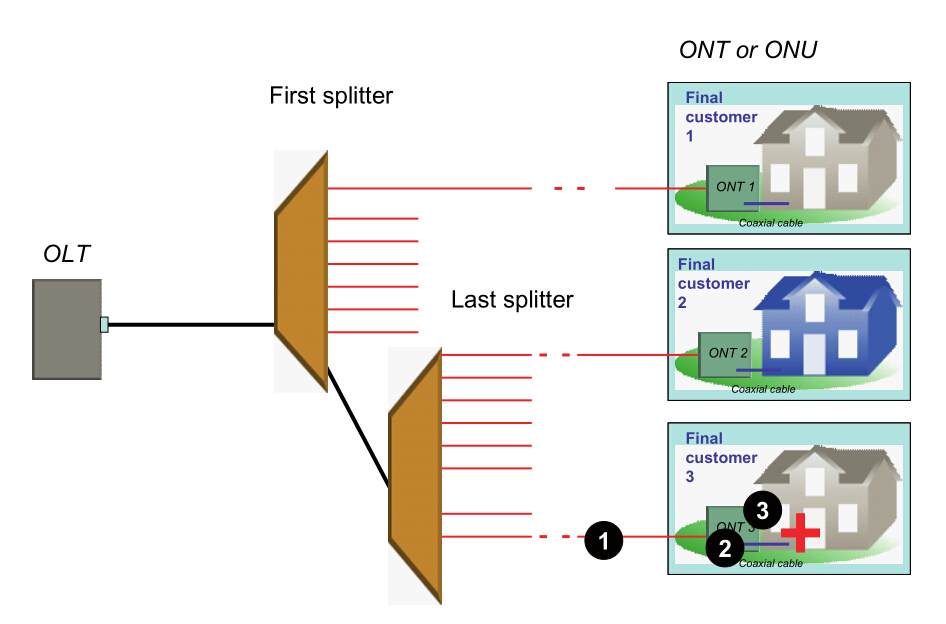
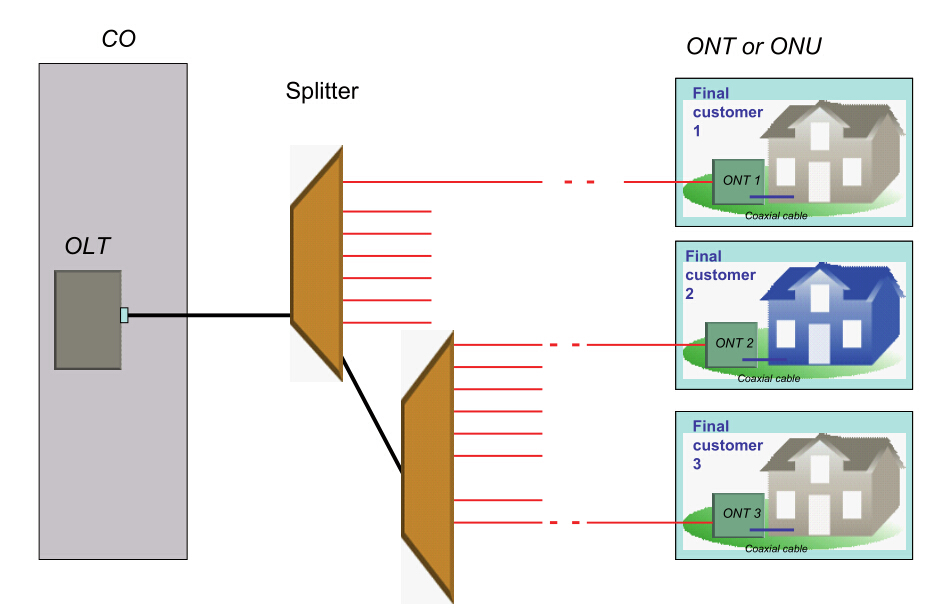
Scenario 2: Cascaded PON (all affected customers are connected to the same splitter)
When all customers connected to the same splitter cannot receive service, but others connected to the same OLT can, the cause may be one of the two—fault at the last splitter, or fault in the fiber link between the cascaded splitters.
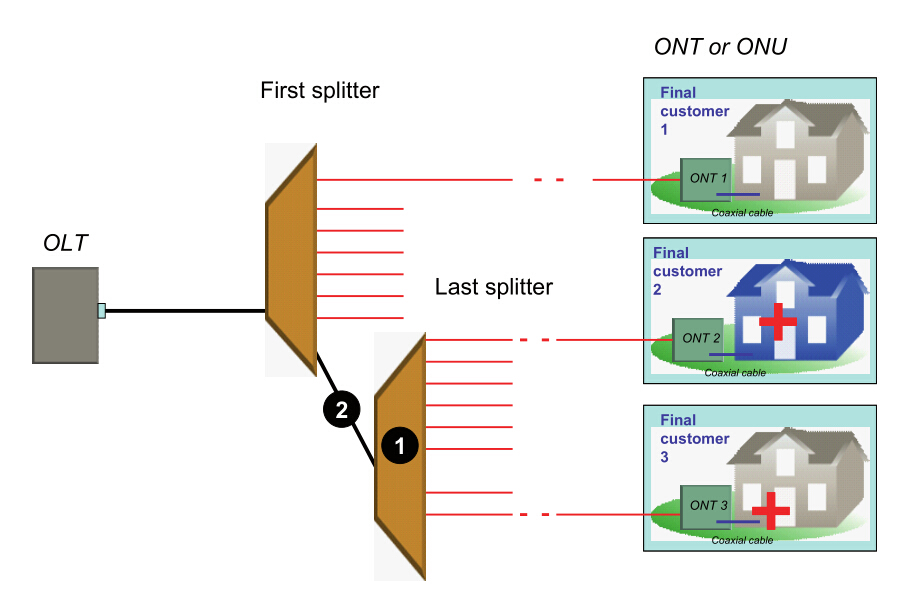
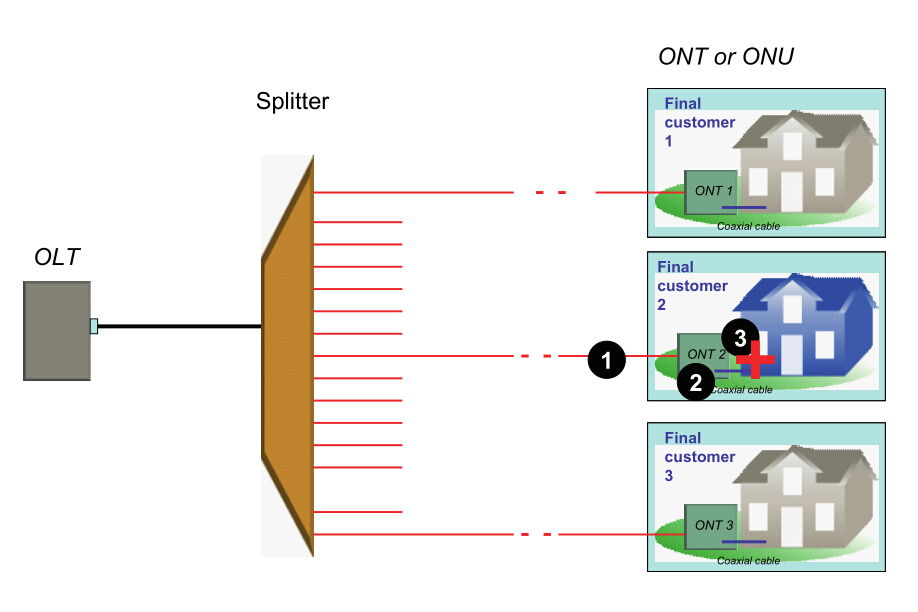
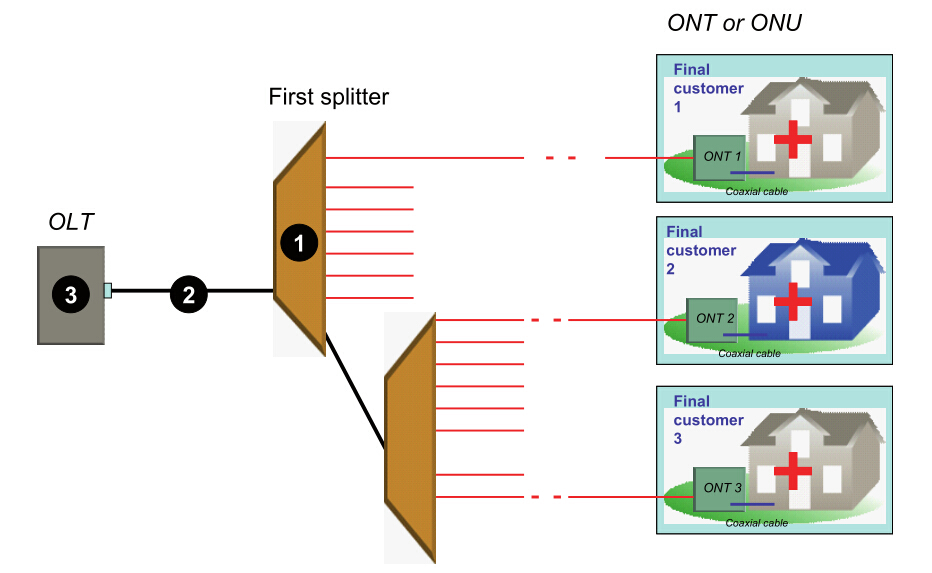
Scenario 3: All customers are affected (at the OLT level)
Whether or not the PON is cascaded, all customers dependent on the same OLT may be affected. If all customers are affected, the cause may be from of the three—fault in the splitter closest to the OLT, or fault in the feeder fiber cable of the network, or fault in the OLT equipment.
PON Troubleshooting Basics
Troubleshooting a PON first involves locating and identifying the source of an optical problem. The following picture offers a complete view of all of the possible fault locations depending on how many customers are affected, and the best location to shoot an OTDR.
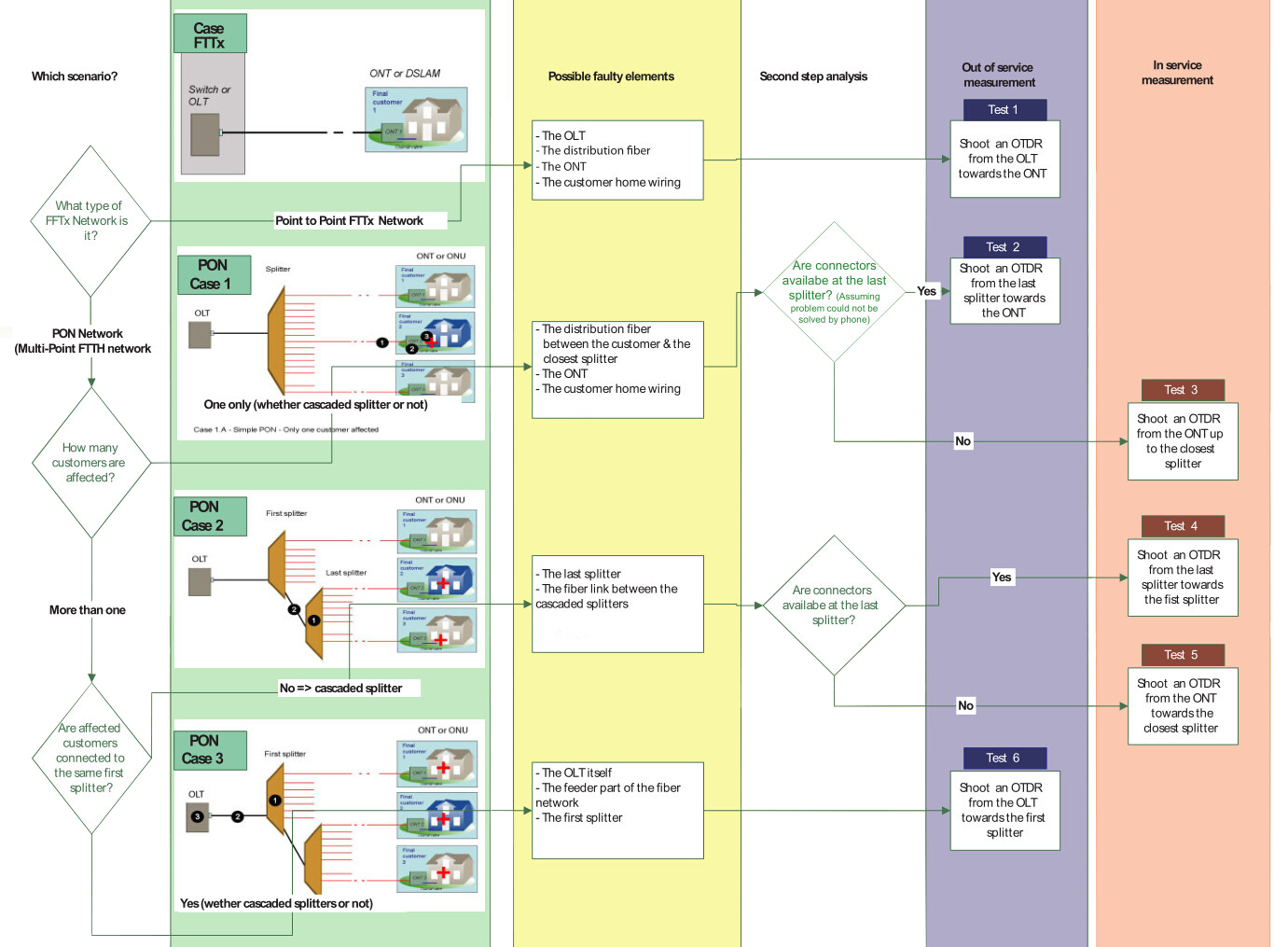
Generally, most PON problems can be located using PON power meter and PON-optimized OTDR. The power meter is connected as a pass-through device, allowing both downstream and upstream traffic to travel unimpeded. It measures the power at each wavelength simultaneously and can be used for troubleshooting at any point in the network. A monitoring OTDR provides a graphical trace that enables to locate and characterize every element in a link, including connectors, splices, splitters, couplers and faults. OTDRs designed specifically for in-service PON troubleshooting exist. These OTDRs feature a dedicated port for testing at 1625 or 1650 nm and incorporate a filter that rejects all unwanted signals (1310, 1490 and 1550 nm) that could contaminate the OTDR measurement. Only the OTDR signal at 1625 or 1650 nm is allowed to pass through the filter, generating a precise OTDR measurement. In-service OTDR troubleshooting of optical fiber should be done in a way that does not interfere with the normal operation and expected performance of the information channels. Testing with the 1625 or 1650nm wavelength does just that. A PON-optimized OTDR does not interfere with the CO’s transmitter lasers because the 1650nm wavelength complies with the ITU-T L.41 Recommendation. The addition of a broadband filter, acting as a 1625 or 1650nm testing port at the CO’s WDM coupler, may be beneficial. And the quality of service provided to other subscribers serviced by the same 1xN splitter is not affected. Consequently, the technician can connect the OTDR’s 1625 or 1650nm port to the ONT and send the signal toward the CO. If a 1625 or 1650nm testing port is added to the CO, it is also possible to perform tests from the CO down to the ONT, but a 1625 or 1650nm filter may be needed at each ONT.Summary
READ MORE ...Fiber Optic Patch CablesPON troubleshooting should first find the fault locations of the network. This post lists three types of potential fault scenarios for your reference. After knowing where the fault is, then you should use the correct tools to test and verify. PON power meter and OTDR can help significantly during the testing process. If you are confused about PON troubleshooting, hope the information in this post will be helpful.
- Customers Reviews
* Delivery Time.
We need 1-2 days to process your order before shipping. There are two shipping methoed.
Fast Delivery: The delivery time for US, European countries the delivery will take 3-5 days.
Slow Delivery: The delivery time for US, European countries the delivery will take 7-15 days.
* Tracking information.
After we ship package, customer receive automatic email with tracking details.
* Lost Package Policy.
If a package did not arrive in 2 weeks after the shipping date, then this package is treated as Lost. In this case a new package will be shipped to the customer provided we are able to give the same items as those purchased by the customer. If we are not able to provide the same items to substitute the lost ones we will either propose to the customer similar items or refund their cost as it will be mutually agree with the customer. If one or more items neither the same nor similar are available to be shipped, the customer can request to cancel the order entirely, thus the total cost of the order including shipping and handling cost will be fully refunded.























































































 (0)
(0) (0)
(0) (0)
(0) (0)
(0) (0)
(0)